Automate Chromatic with GitHub Actions
Chromatic provides a GitHub Action to help you automate your visual regression tests and publish Storybook.
Workflow setup
In your .github/workflows directory, create a new file called chromatic.yml and add the following:
name: "Chromatic"
on: push
jobs:
chromatic:
name: Run Chromatic
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v5
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- uses: actions/setup-node@v6
with:
node-version: 24.13.0
- name: Install dependencies
# ⚠️ See your package manager's documentation for the correct command to install dependencies in a CI environment.
run: npm ci
- name: Run Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
# ⚠️ Make sure to configure a `CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN` repository secret
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}name: "Chromatic"
on: push
jobs:
playwright:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
container:
image: mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:v1.58.0-noble
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v5
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- uses: actions/setup-node@v6
with:
node-version: 24.13.0
- name: Install dependencies
# ⚠️ See your package manager's documentation for the correct command to install dependencies in a CI environment.
run: npm ci
- name: Run Playwright tests
run: npx playwright test
env:
HOME: /root
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
if: always()
with:
# Chromatic automatically defaults to the test-results directory.
# Replace with the path to your custom directory and adjust the CHROMATIC_ARCHIVE_LOCATION environment variable accordingly.
name: test-results
path: ./test-results
retention-days: 30
chromatic:
name: Run Chromatic
needs: playwright
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v5
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- uses: actions/setup-node@v6
with:
node-version: 24.13.0
- name: Install dependencies
# ⚠️ See your package manager's documentation for the correct command to install dependencies in a CI environment.
run: npm ci
- name: Download Playwright test results
uses: actions/download-artifact@v4
with:
name: test-results
path: ./test-results
- name: Run Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
# ⚠️ Enable Playwright
playwright: true
# ⚠️ Make sure to configure a `CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN` repository secret
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
# ⚠️ Optionally configure the archive location with env vars
env: CHROMATIC_ARCHIVE_LOCATION=./test-resultsname: "Chromatic"
on: push
jobs:
cypress:
name: Run Cypress
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
container:
image: cypress/browsers:node-24.13.0-chrome-143.0.7499.192-1-ff-147.0-edge-143.0.3650.139-1
options: --user 1001
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v5
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- uses: actions/setup-node@v6
with:
node-version: 24.13.0
- name: Install dependencies
# ⚠️ See your package manager's documentation for the correct command to install dependencies in a CI environment.
run: npm ci
- name: Run Cypress tests
uses: cypress-io/github-action@v7
env:
ELECTRON_EXTRA_LAUNCH_ARGS: "--remote-debugging-port=9222"
with:
start: npm run dev
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
# Chromatic automatically defaults to the cypress/downloads directory.
# Replace with the path to your custom directory and adjust the CHROMATIC_ARCHIVE_LOCATION environment variable accordingly.
name: test-results
path: ./cypress/downloads
retention-days: 30
chromatic:
name: Run Chromatic
needs: cypress
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v5
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- uses: actions/setup-node@v6
with:
node-version: 24.13.0
- name: Install dependencies
# ⚠️ See your package manager's documentation for the correct command to install dependencies in a CI environment.
run: npm ci
- name: Download Cypress test results
uses: actions/download-artifact@v4
with:
name: test-results
path: ./cypress/downloads
- name: Run Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
# ⚠️ Enable Cypress
cypress: true
# ⚠️ Make sure to configure a `CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN` repository secret
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
# ⚠️ Optionally configure the archive location with env vars
env:
CHROMATIC_ARCHIVE_LOCATION: ./cypress/downloadsThis is a fairly basic setup. More advanced options are explained below.
Project token secret
To securely provide the projectToken to Chromatic, you must configure a GitHub repository secret. First, find your project on Chromatic.com and go to Manage and then Configure. Copy the project token.
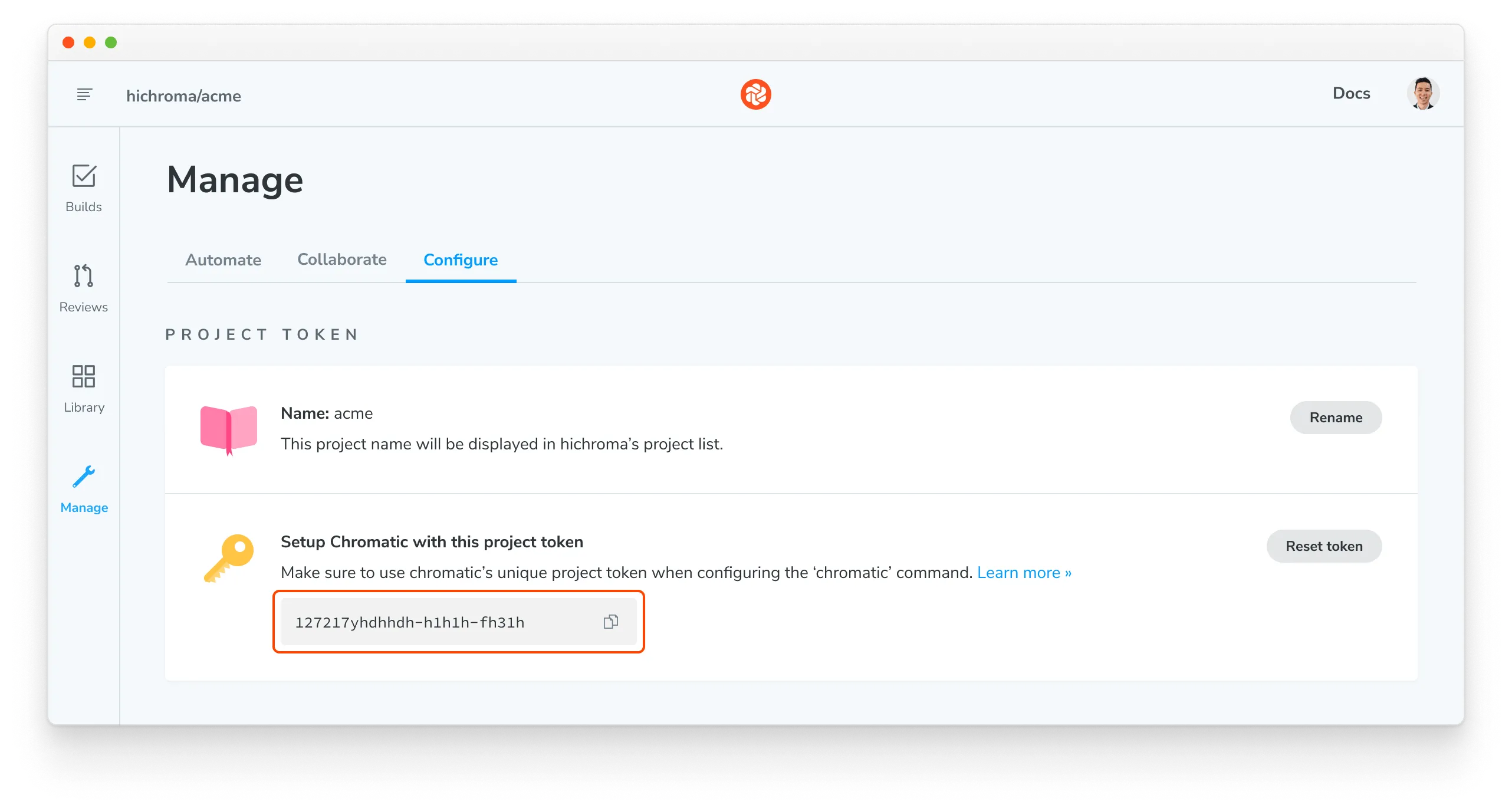
On GitHub, go to the Settings tab on your repository. Under Security, find Secrets and variables and then Actions. Click New repository secret.
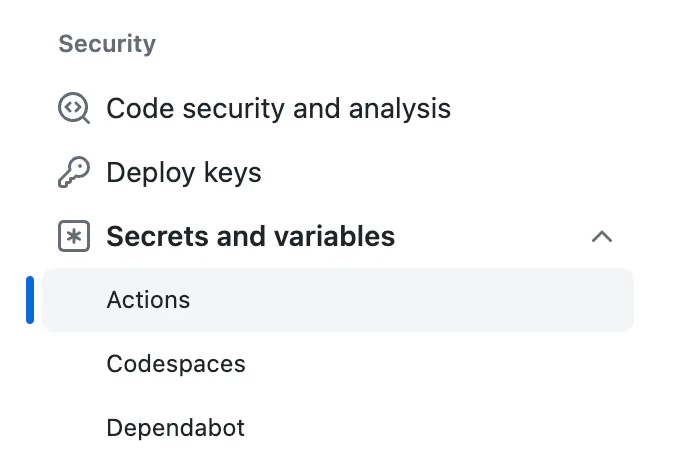
Set CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN as the Name and paste the project token as the Secret. Click Add secret to save the value.
Read the official GitHub secrets documentation.
Forked repositories
GitHub secrets work at a repository level. Forked repositories will not have access to them. If you want to run Chromatic on cross-repository (forked) PRs, you’ll have to expose the projectToken by including it as plaintext in your chromatic.yml workflow file. Be aware that anyone with access to this file will be able to run Chromatic builds on your project, consuming your snapshot quota. You can reset the project token on the Manage > Configure screen at any time if you think it may have been compromised.
Pinning the CLI version
While the CLI follows semantic versioning, the GitHub Action typically auto-upgrades to the latest version. However, it’s possible to pin the CLI version by changing the tag:
- To automatically receive all new updates, use
chromaui/action@latest(the default). - To automatically receive new features and bugfixes but avoid breaking changes, use
chromaui/action@vXwherevXis a major version number (e.g.v10). - To not receive any updates but pin the action to a specific CLI version, use
chromaui/action@vX.Y.ZwherevX.Y.Zis a full semver version (e.g.v10.0.0).
The full list of tags is available on GitHub.
Configuration
For more information on the available options, refer to our configuration reference documentation.
Outputs
Chromatic’s GitHub Action returns some information about your build in the form of outputs. The table below lists what’s currently available. Read the official GitHub documentation for more information about outputs.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| url | string | An alias for the build URL.https://www.chromatic.com/build?appId=example-app-id&number=100 |
| buildUrl | string | The build URL. https://www.chromatic.com/build?appId=example-app-id&number=100 |
| storybookUrl | string | The Storybook preview URL for your current branch / Pull Request.https://main--example-app-id.chromatic.com |
| code | string | The exit code for the current run of the Chromatic CLI. |
| actualCaptureCount | number | The number of captured snapshots. |
| changeCount | number | The number of tests with visual changes, including any inherited changes (e.g., due to TurboSnap). |
| componentCount | number | The number of components in the published Storybook. |
| errorCount | number | The number of tests with error(s), including any inherited errors (e.g., due to TurboSnap). |
| inheritedCaptureCount | number | The number of inherited (not captured) snapshots (e.g., due to TurboSnap). |
| interactionTestFailuresCount | number | The number of stories with interaction test failures. |
| specCount | number | The number of stories in the published Storybook. |
| testCount | number | The number of tests on the build. |
Run Chromatic on specific branches
If you need to customize your workflow to run Chromatic on specific branches, adjust your workflow like so:
name: "Chromatic"
# 👇 Workflow event to trigger execution
on:
push:
branches-ignore:
- "example" # 👈 Excludes the example branchRead the official GitHub branch workflow documentation.
Now Chromatic will run for any branch except example.
Other branches, such as the ones created by the Renovate bot, can also be included.
Run Chromatic on large projects
Chromatic is prepared to handle large file uploads (with a limit of 5000 files, including stories and assets). If your project exceeds this limit, we recommend enabling the zip option in your workflow to compress your build before uploading it. For example:
jobs:
chromatic:
steps:
# ... other steps
- uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
# 👇 Runs Chromatic with the option to compress the build output.
zip: trueRun Chromatic on monorepos
Chromatic can be run on monorepos that have multiple subprojects. Each subproject will need its project token.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you’re in the correct working directory for the subproject.
- Have the
build-storybooknpm script in the subproject’spackage.jsonfile OR explicitly name the script using thebuildScriptNameparameter and ensure the script is listed in the subproject’spackage.jsonfile.
If you’ve already built your Storybook in a separate CI step, you can alternatively point the action at the build output using the storybookBuildDir parameter.
jobs:
chromatic:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
# ... other steps
- name: Publish Project 1 to Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
# 👇 Chromatic projectToken, refer to the manage page to obtain it.
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN_1 }}
workingDir: packages/project_1
- name: Publish Project 2 to Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
# 👇 Chromatic projectToken, refer to the manage page to obtain it.
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN_2 }}
workingDir: packages/project_2If you want to run Chromatic in parallel for each subproject, you will need to create separate workflow files.
# 👇 Customize the workflow name
name: "Chromatic 1"
on: push
jobs:
chromatic:
steps:
# ... other steps
- name: Run Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
# 👇 Chromatic projectToken, refer to the manage page to obtain it.
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN_1 }}
workingDir: packages/project_1# 👇 Customize the workflow name
name: "Chromatic 2"
on: push
# List of jobs
jobs:
chromatic:
steps:
# ... other steps
- name: Run Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
# 👇 Chromatic projectToken, refer to the manage page to obtain it.
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN_2 }}
workingDir: packages/project_2Enable TurboSnap
TurboSnap is an advanced Chromatic feature implemented to improve the build time for large projects. By default, it is disabled in your CI environment. To enable it, add the onlyChanged option to the workflow as follows:
jobs:
chromatic:
steps:
# ... other steps
- name: Run Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
onlyChanged: true # 👈 Required option to enable TurboSnapTurboSnap is highly customizable and can be configured to fit your requirements. For more information, read our documentation.
Trigger full rebuilds
By default, TurboSnap relies on Webpack’s dependency graph to determine which files changes since the last build. If you’re working with files processed outside the scope of Webpack (e.g., fonts, images, CSS, external libraries), you can use the externals option to tell Chromatic to rebuild the entire project when a file matching the pattern is changed. For example:
# Other necessary configuration
jobs:
chromatic:
steps:
# ... other steps
- name: Run Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
onlyChanged: true # 👈 Required option to enable TurboSnap
externals: packages/(icons/icons|tokens/src)/**Multiple file patterns can also be provided as follows:
# ... other config
- name: Run Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
onlyChanged: true # 👈 Required option to enable TurboSnap
externals: |
*.sass
public/**The externals option also accept additional glob patterns defined via picomatch. See the globs guide for more info.
Support for environment variables
Environment variables are supported in Chromatic. You can use them to customize your workflow execution or provide project-related variables (e.g., API URLs). Add the env key in the workflow file and provide the necessary variables to enable them. For example:
jobs:
chromatic:
steps:
# ... other steps
- uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
env:
# 👇 Sets environment variables
CHROMATIC_RETRIES: 5
LOG_LEVEL: "error"For more information on the environment variables supported by Chromatic, refer to our configuration reference documentation.
It comes with a caveat if you need to provide project-specific environment variables. We recommend that you prefix each variable with the STORYBOOK keyword and adjust your workflow to the following:
jobs:
chromatic:
steps:
# ... other steps
- uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
env:
# 👇 Sets the environment variable
STORYBOOK_SOME_ENV_VAR: ${{ secrets.STORYBOOK_SOME_ENV_VAR }}Read the official Storybook environment variable’s documentation.
Fail workflow if changes are found
If you are using pull request statuses as required checks before merging, you may want your workflow step to fail if test snapshots show changes. By default, Chromatic exits with code 0 if changes are detected. We expect users to review these changes and decide whether to accept or reject them. However, if you prefer the workflow to fail when changes are found, you can use the exitZeroOnChanges option. For example:
# Other necessary configuration
jobs:
chromatic:
steps:
# ... other steps
- name: Run Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
exitZeroOnChanges: false # 👈 Fail workflow if changes are foundRead about the available options.
Re-run failed builds after verifying UI test results
Builds that contain visual changes need to be verified. The task will fail if exitZeroOnChanges option is set to false. Once you accept all the changes, re-run the workflow, and the chromatic job will pass.
If you deny any change, you will need to make the necessary code changes to fix the test (and thus start a new run) to get Chromatic to pass again.
Recommended configuration for build events
GitHub’s Actions, like other CI systems, can run based on any type of event. Our recommendation is to run Chromatic’s step on push events.
While the pull_request event also works, it can cause Chromatic’s baselines to be lost in certain scenarios or cause Chromatic to use an unexpected baseline from the main branch.
GitHub allows workflows to execute on commits pushed to a branch in a pull request or on “merge” commits between that branch and the base branch (main). These merge commits do not persist in your repository’s history. When a GitHub action is triggered on pull_request, GitHub creates an ephemeral branch and merges the PR branch into the latest from main. For details, refer to the pull request workflow docs to understand what GITHUB_SHA and GITHUB_REF are set to.
This means the latest build on main will be an ancestor of this ephemeral branch, even though it is not an ancestor of the actual PR branch. Therefore, it’ll use the incorrect baseline for comparison. That’s why we recommend running Chromatic using the push event.
If you decide to use the pull_request event, we recommend creating a separate workflow for Chromatic using the following strategy for the checkout step:
- uses: actions/checkout@v5
with:
fetch-depth: 0
# 👇 Tells the checkout which commit hash to reference
ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.ref }}
env:
CHROMATIC_BRANCH: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.ref || github.ref_name }}
CHROMATIC_SHA: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha || github.ref }}
CHROMATIC_SLUG: ${{ github.repository }}NOTE: The ref on the checkout step is required for TurboSnap to correctly detect changed files.
The pull_request event makes an ephemeral commit between latest main and the commit you have created. This means our git diff will include everything that’s happened on main since you branched. That’s what the ref solution solves for.
Here is the scenario:
What’s happened:
The user creates P off A (main) with 2 files changed.
When the GitHub Action runs on the pull_request event, by default it creates a new merge commit P'.
When we take the git diff between P' and the baseline from main (A) we are not going to just get the changes in P but also all the changes in B, C and D.
UI Test and UI Review
UI Tests and UI Review rely on branch and baseline detection to keep track of snapshots. We recommend the following configuration.
Maintain a clean “main” branch
A clean main branch is a development best practice and highly recommended for Chromatic. This means testing your main branch to ensure builds are passing. It’s important to note that baselines will not persist through branching and merging unless you test your main branch.
If the builds result from direct commits to main, you must accept changes to keep the main branch clean. If they’re merged from feature-branches, you must ensure those branches are passing before you merge into main.
GitHub squash/rebase merge and the “main” branch
GitHub’s squash/rebase merge functionality creates new commits that have no association with the branch being merged. If you’ve enabled our GitHub application in the UI Review workflow, then we will automatically detect this situation and bring baselines over (see Branching and Baselines for more details).
If you’re using this functionality but notice the incoming changes were not accepted as baselines in Chromatic, then you’ll need to adjust the workflow to include a new step with the autoAcceptChanges option. For example:
jobs:
chromatic:
steps:
# ... other steps
- name: Run Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
autoAcceptChanges: "main" # 👈 Option to accept all changes on mainRead about the available options.
Including the autoAcceptChanges option ensures all incoming changes will be accepted as baselines. Additionally, you’ll maintain a clean main branch.
If you want to test the changes introduced by the rebased branch, you can adjust your workflow and include a new step with the ignoreLastBuildOnBranch option. For example:
jobs:
chromatic:
steps:
# ... other steps
- name: Run Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
ignoreLastBuildOnBranch: "my-branch" # 👈 Option to ignore the last build on target branchRead about the available options.
Including the ignoreLastBuildOnBranch option ensures the latest build for the specific branch is not used as a baseline.
Run Chromatic on external forks of open source projects
You can enable PR checks for external forks by sharing your project token where you configured the Chromatic command (often in package.json or in the pipeline step).
Sharing project tokens allows contributors and others to run Chromatic builds on your project, consuming your snapshot quota. They cannot access your account, settings, or accept baselines. This can be an acceptable tradeoff for open source projects that value community contributions.
Skipping builds for certain branches
Sometimes you might want to skip running a build for a certain branch but still have Chromatic mark the latest commit on that branch as “passed”. Otherwise, pull requests could be blocked due to required checks that remain pending. To avoid this issue, you can run chromatic with the --skip flag. This flag accepts a branch name or glob pattern.
For instance, Dependabot automatically updates the dependencies of a project. Although some dependencies can result in UI changes, you might not find it worthwhile to run Chromatic for every dependency update. Instead, you could rely on Chromatic running against the main or develop branch. One use case for this feature is skipping builds for branches created by a bot.
To skip builds for dependabot branches, use the following:
jobs:
chromatic:
steps:
# ... other steps
- name: Run Chromatic
uses: chromaui/action@latest
with:
projectToken: ${{ secrets.CHROMATIC_PROJECT_TOKEN }}
skip: "dependabot/**" # 👈 Option to skip Chromatic for certain branchesTo apply this to multiple branches, use an “extended glob”. See the globs guide for details.
skip: "@(renovate/**|dependabot/**)"Read about the available options.